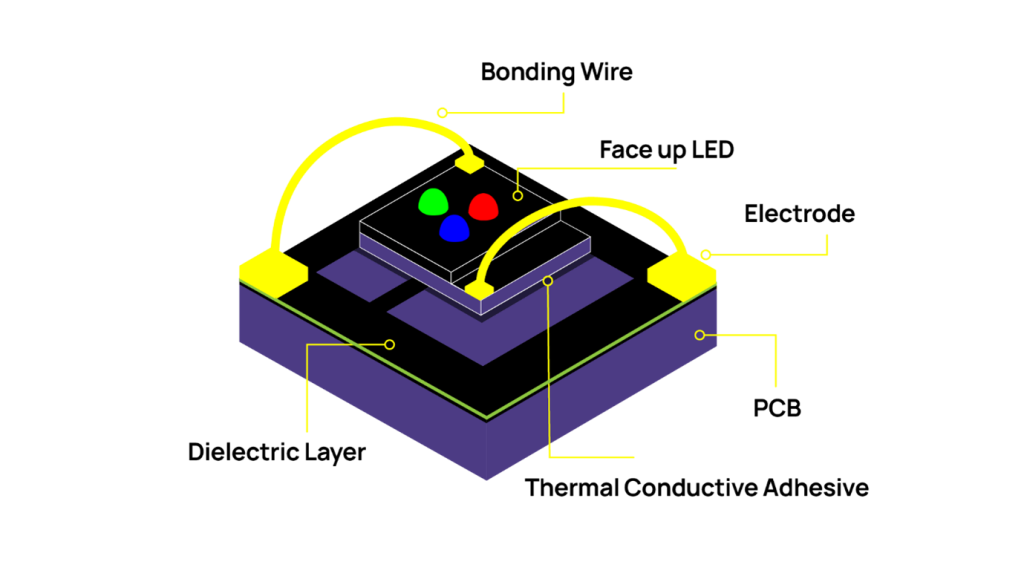
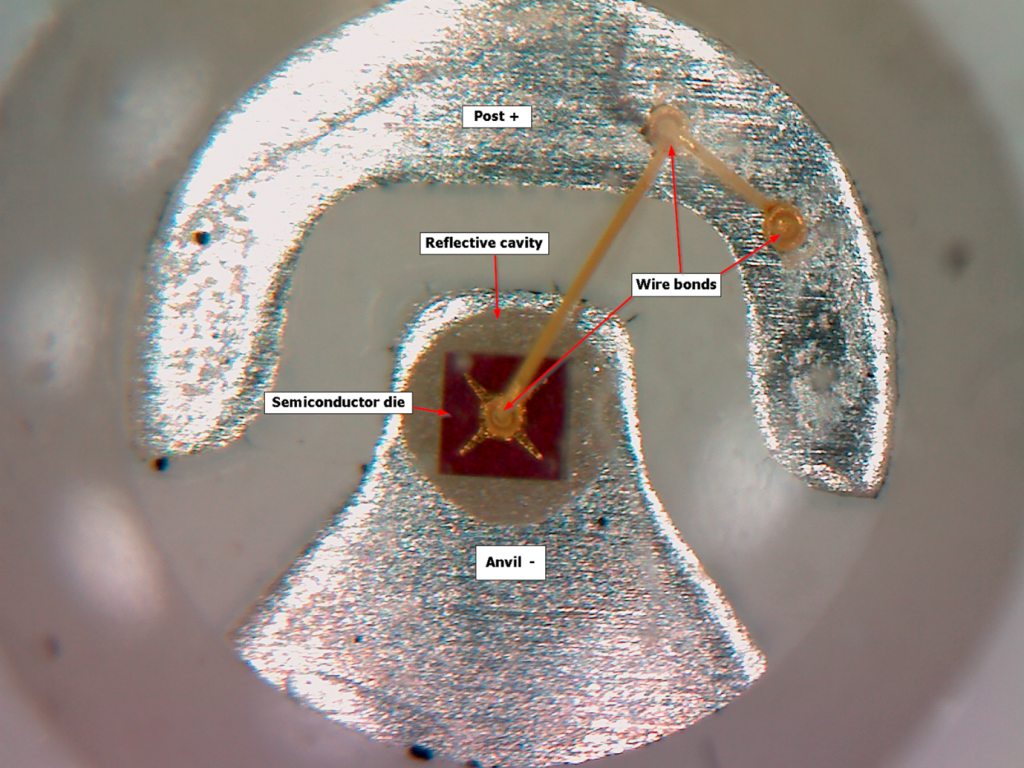
What Are Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) LEDs?
SMD stands for Surface-Mounted Device. In an SMD LED, the red, green and blue light sources are housed together within a single, compact LED package that is mounted directly onto the circuit board.
This integrated design allows pixels to be placed closer together, which is essential for achieving high resolution and detailed images.
How SMD LEDs Create High-Resolution Images
Because all three colours sit within one small package, SMD LEDs:
- Enable smaller pixel pitch
- Improve colour blending at close distances
- Reduce visible pixel separation
This makes images appear smoother and more uniform, especially when viewed from short distances.
Key Advantages of SMD LEDs
- High resolution for detailed content
- Wide viewing angles, maintaining colour accuracy off-axis
- Smooth colour mixing at close range
- Slim, lightweight cabinets for indoor installations
These advantages make SMD LEDs ideal for environments where viewers are close to the screen.
Typical Applications
SMD LEDs are commonly used in:
- Indoor feature walls
- Retail environments
- Corporate lobbies
- Broadcast and studio displays
- Exhibition and event screens
They are particularly effective where image quality and visual impact matter more than extreme brightness.
Limitations of SMD LEDs
While highly versatile, SMD LEDs:
- Are less impact-resistant than DIP LEDs
- Require additional protection in harsh outdoor environments
- May need encapsulation (such as GOB) for public-facing installations
Choosing SMD LEDs should always consider environment, access and risk level.
When to Choose SMD LEDs
SMD LEDs are the right choice when:
- Viewers are close to the screen
- High resolution is essential
- Indoor image quality is the priority