Pixel Pitch (Pixel LED) How pixel spacing affects image quality and viewing distance
Pixel pitch is one of the most important technical specifications of an LED screen. It directly affects image sharpness, viewing distance and overall cost, making it a critical factor when choosing the right LED display for any environment.
What Is Pixel Pitch?
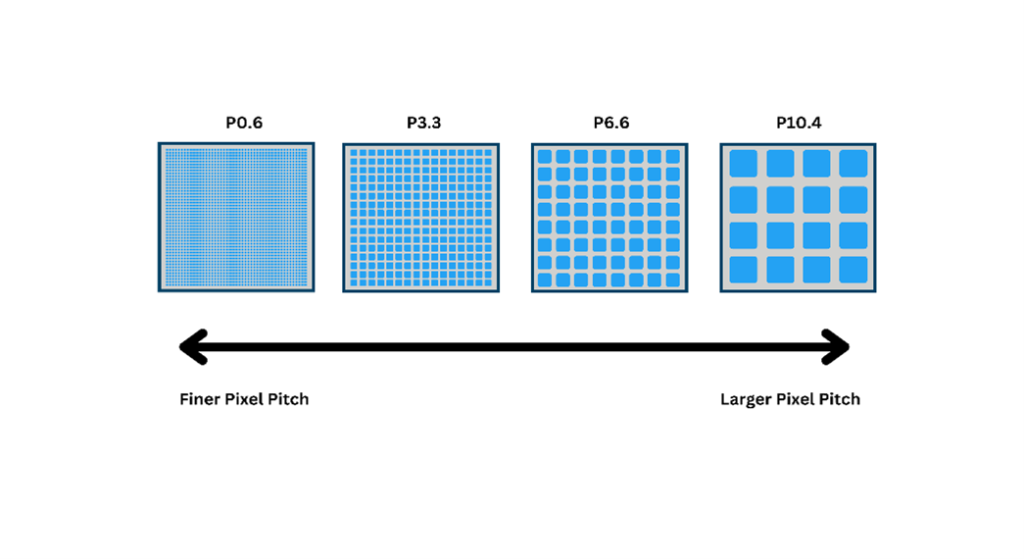
Pixel pitch refers to the distance between the centres of two adjacent pixels, measured in millimetres (mm).
For example:
- P1.5 = 1.5 mm between pixels
- P3 = 3 mm between pixels
- P6 = 6 mm between pixels
The smaller the number, the closer the pixels are together and the higher the potential image detail.
Why Pixel Pitch Matters
Pixel pitch determines:
- How sharp an image appears
- How close viewers can stand to the screen
- Whether individual pixels are visible
- The overall cost of the display
It matters more than resolution alone, because LED screens are built to physical dimensions, not fixed pixel counts.
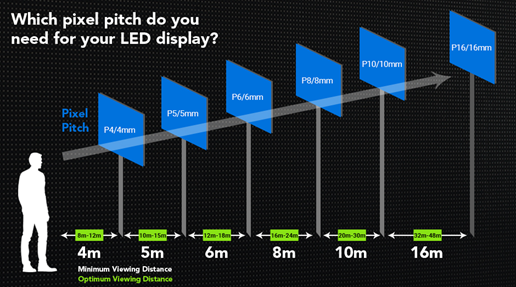
Pixel Pitch and Viewing Distance
As a general rule:
- Smaller pixel pitch = closer viewing distance
- Larger pixel pitch = longer viewing distance
If viewers are too close to a screen with a large pixel pitch, individual pixels become visible and the image appears coarse.
Conversely, specifying a very fine pixel pitch for a long-distance application often adds cost without delivering visible benefits.
Typical Pixel Pitch Ranges
Fine Pixel Pitch (≤1.5 mm)
Used where viewers are very close to the screen and image detail is critical.
Common environments include control rooms, broadcast studios and boardrooms.
Standard Indoor Pixel Pitch (1.8–3 mm)
The most common range for indoor LED screens, balancing image quality and cost.
Often used in retail, corporate and exhibition spaces.
Large Pixel Pitch (4 mm and above)
Designed for long viewing distances and outdoor environments, where brightness and visibility matter more than fine detail.
Pixel Pitch vs Resolution
Unlike LCD screens, LED screens do not have a fixed resolution. The resolution depends on:
- Pixel pitch
- Physical screen size
Two LED screens with the same physical size but different pixel pitches will have very different resolutions.
This is why pixel pitch is usually a more useful specification than resolution when comparing LED displays.
Cost Considerations
Smaller pixel pitch screens:
- Use more LEDs per square metre
- Require more complex electronics
- Cost significantly more
For this reason, the best pixel pitch is not always the smallest; it is the one that matches the viewing distance and content requirements.
Content and Pixel Pitch
Pixel pitch should also align with content type:
- Text-heavy or detailed graphics benefit from smaller pixel pitch
- Large visuals, video and bold messaging can work well with larger pitch
Understanding how content will be viewed is just as important as understanding the specification.
Common Misconceptions About Pixel Pitch
“Lower pixel pitch always means better quality”
Only if the viewing distance supports it. Beyond a certain point, finer pitch delivers no visible improvement.
“Pixel pitch and resolution are the same thing”
They are related, but not the same. Pixel pitch defines pixel spacing; resolution depends on both pitch and screen size.
Choosing the Right Pixel Pitch
Pixel pitch should be selected based on:
- Viewing distance
- Screen size
- Environment (indoor or outdoor)
- Content type
- Budget
A well-matched pixel pitch ensures the screen performs as intended without unnecessary cost or complexity.
Why Pixel Pitch Is One of the Most Important LED Specs
Pixel pitch influences almost every aspect of an LED screen’s performance, from image quality and viewing comfort to cost and scalability. Getting it right is essential for a successful installation.